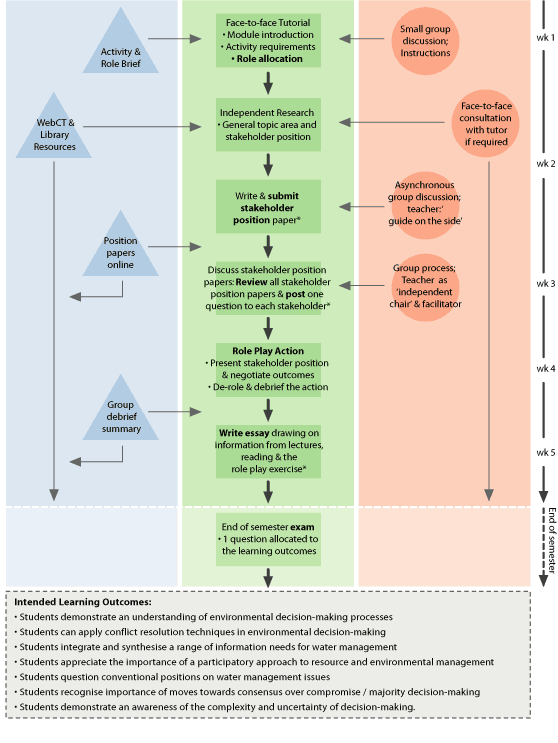
|
ACCESSIBLE RESOURCES
- Formal literature: This mainly takes the form of journal
articles on broad biophysical and institutional issues in
resource management with particular application to river
management. These resources are made available in week one
via electronic reserve in the library. These resources provide
an underpinning in key concepts such as adaptive management
and ecosystem approaches.
- Web-based material: These resources are usually more directly
relevant to the round table scenario itself, such as government
reports and discussion papers, providing more immediate
contextual material. (This material is provided via links
to the WebCT site).
- 'Grey literature' - in particular, material produced by
the management body itself in the form of unpublished reports,
scoping papers etc. This provides direct information on
the case study itself. This material is provided in library
reserve in hard copy.
- Students are also required to conduct independent research
and identify supporting material for their own position
paper as stakeholders. At least three such sources are required.
- Lecture material and background briefing and information
papers, plus a debriefing summary provided on WebCT. Lecture
material supplements both the formal and web-based material
identified above.
Characteristics of the online environment:
The subject WebCT site is arranged as a graphic interface
that visually represents a meeting situation. Each name around
the table represents a stakeholder position, which is linked
to a pop-up window that can be edited by the student assigned
to the role. This functionality facilitates the posting of
each stakeholder position and enables student revisions following
other stakeholder questions.
Some sample screen shots are as follows:
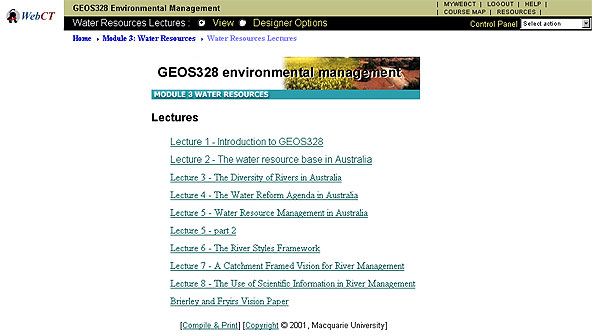

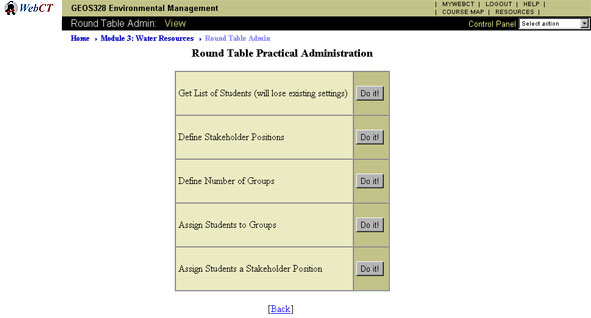
There is an administrative interface that the lecturer uses
to allocate students to groups and roles. The program allows
the lecturer to participate in the activity as an independent
observer
RESOURCES IN CONTEXT
A key challenge presented to students is to relate the resource
set as presented to related material, asking them to frame
the specific situation presented in the round table exercise
in light of broader themes in environmental management. The
specific material is based upon field research that creates
a high level of realism and currency. A balance is sought
between provision of core resources to students and independent
enquiry. All students are required to use a relevant referred
article to substantiate their position paper - something that
is not referred to elsewhere in the course. Broadening the
information base, and sharing these resources with other students,
is promoted.
A major aim is to demonstrate that different stakeholders
use different types of information, but that ultimately one
or more decisions can emerge. Unravelling complexities and
uncertainties in this diverse information base is a key issue
in natural resource management.
VARYING THE RESOURCE SET
The resource set provides the foundational (basic) material
that students need in order to adequately prepare for the
activity (i.e. sufficient signposts/scaffolding). Each student
is expected to research the stakeholder role that they have
been allocated and the position paper must use at least 3
additional references to those provided.
|